- Shanghai, China
- [email protected]
- +86-21-58189111
development history
In the 1940s, Valls and Craig initiated the origin of spinal endoscopy with the use of a cannula for deep tissue biopsy through a posterolateral approach to the lumbar spine. In the late 1980s, Kambin developed the concept of the safety triangle for the foramen and, using endoscopic techniques, performed lumbar discectomy. In 1997, Yeung applied the third generation of spinal endoscopy to the clinic. This technique emphasized the first step of entering the intervertebral disc through the "safety triangle" to decompress, and then gradually removing the nucleus pulposus tissue from the inside to the outside under the surveillance of the endoscope. This operation method is called. YES technology.
In 2003, German Professor Hoogland and others aimed at the deficiencies of YESS technology, and invented THESSYS system/technology (Thomas Hoogland Endoscopic Spinal System, TESS technology) on the basis of YESS technology, through the removal of part of the facet joints into the epidural space, from the epidural The intervertebral disc tissue is sequentially removed from the cavity into the intervertebral disc (outside-in technique). This technique is not blocked by the facet joint after excision of the articular process, and can directly decompress the compressed nerve root. Therefore, it is more suitable for patients with huge protrusion, prolapse, and dissociation, and the curative effect is more accurate.
Foraminal Indications
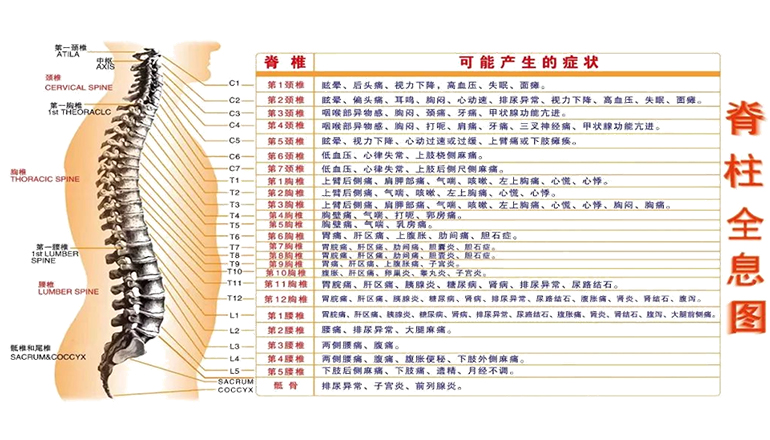
1. Lumbar intervertebral disc herniation: compression of nerves, resulting in low back pain, low back pain, limited walking, intermittent claudication, etc.
2. Lumbar discogenic low back pain: that is, the herniation of the intervertebral disc is not obvious, but the low back pain is obvious, recurring, and conservative treatment is ineffective. At this point, the intervertebral disc has been structurally damaged, causing pain.
3. Lumbar intervertebral foraminal stenosis: In middle-aged and elderly patients with low back and leg pain, intervertebral foraminal bone spurs or ligament hypertrophy may cause intervertebral foraminal stenosis, resulting in blocked nerve passages. Enlarged intervertebral foramen for nerve decompression
Contraindications for foraminal endoscopy:
1. Intervertebral disc herniation combined with spinal stenosis.
2. Intervertebral disc herniation combined with segmental instability.
3. Accompanied by obvious multi-segment degeneration.
Leave a Comments