- Shanghai, China
- [email protected]
- +86-21-58189111
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to remove the gallbladder, which is a small organ located under the liver that stores and releases bile. This procedure is typically performed using a laparoscope, which is a long, thin tube with a camera and surgical instruments attached, inserted through small incisions in the abdomen.
Here are the steps for carrying out laparoscopic cholecystectomy:
Preparation: The patient is placed under general anesthesia, and the surgeon makes several small incisions in the abdomen to insert the laparoscope and other surgical instruments.
Exploration of the abdomen: The surgeon uses the laparoscope to explore the abdominal cavity and locate the gallbladder.
Dissection of the cystic duct and artery: The surgeon carefully dissects the cystic duct and artery, which are the two structures that connect the gallbladder to the bile duct and liver.
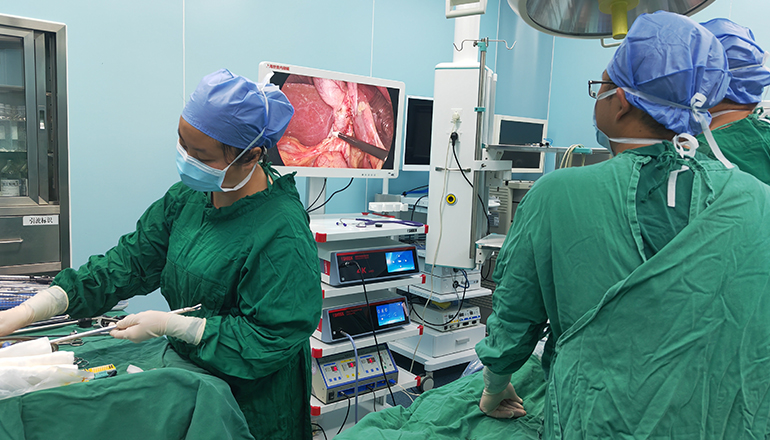
Removal of the gallbladder: Once the cystic duct and artery have been cut, the surgeon gently removes the gallbladder from the liver.
Closure of the incisions: The small incisions are closed using sutures or surgical glue.
Drain placement: In some cases, a drain may be placed in the abdomen to help remove any fluid or bile that may have accumulated during the surgery.
Closure: Finally, the patient is monitored in the recovery room and then transferred to a hospital room. Pain medications are given as needed, and the patient is encouraged to walk around and resume normal activities as soon as possible.
Potential complications: As with any surgical procedure, there are potential risks and complications associated with laparoscopic cholecystectomy. These may include bleeding, infection, bile leak, or damage to surrounding organs. However, these complications are rare, and the benefits of laparoscopic surgery typically outweigh the risks.
Follow-up: The patient will typically be scheduled for a follow-up appointment with their surgeon to monitor their recovery and ensure that there are no complications or signs of infection. Most patients can expect to fully recover within a few weeks and resume their normal activities without restrictions.
Advantages of laparoscopic cholecystectomy: Compared to traditional open surgery, laparoscopic cholecystectomy offers several advantages. These include smaller incisions, less pain and scarring, a shorter hospital stay, and a faster recovery time. In addition, laparoscopic surgery is associated with a lower risk of complications and a lower risk of bile duct injury or other damage to surrounding organs.
Long-term outcomes: After a successful laparoscopic cholecystectomy, patients can expect to live a normal and healthy life, with a low risk of gallstone recurrence. In most cases, patients can return to their normal activities within a few weeks and do not require any dietary or lifestyle changes.
Alternative procedures: In some cases, laparoscopic cholecystectomy may not be appropriate for all patients. For example, patients with extensive scarring from previous surgeries or severe liver disease may require an open cholecystectomy. Additionally, some patients may benefit from a bile duct exploration to remove any stones that have migrated from the gallbladder to the bile duct. Your surgeon will discuss all available options with you to determine the best course of treatment for your individual needs.
Preoperative evaluation: Before undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy, your surgeon will perform a thorough evaluation to ensure that you are a good candidate for the procedure. This may include blood tests, imaging studies, and other diagnostic tests to assess your overall health and the extent of your gallbladder disease.
Postoperative care: After surgery, you will receive detailed instructions on how to care for your incisions, manage pain, and resume normal activities. You will also need to follow a restricted diet for a few days and avoid heavy lifting or strenuous activity for several weeks. Your surgeon will schedule follow-up appointments to monitor your progress and ensure that you are healing properly.
Long-term care: Although laparoscopic cholecystectomy is a relatively safe and effective procedure, some patients may experience long-term complications, such as bile reflux or diarrhea. Your surgeon will work with you to develop a long-term care plan to manage any symptoms and ensure that you remain healthy and active.
In summary, laparoscopic cholecystectomy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to remove the gallbladder, typically with few complications and a fast recovery time. However, like any surgical procedure, it is important to carefully consider the risks and benefits and choose a qualified surgeon with experience in laparoscopic techniques. If you are considering laparoscopic cholecystectomy, talk to your doctor to determine if it may be an appropriate treatment option for you.
Leave a Comments