- Shanghai, China
- [email protected]
- +86-21-58189111
A tubal pregnancy, also known as an ectopic pregnancy, occurs when a fertilized egg implants itself outside of the uterus, most commonly within the fallopian tubes. If left untreated, a tubal pregnancy can lead to life-threatening complications such as internal bleeding and ruptured fallopian tubes.
Conservative operation of a tubal pregnancy involves using a gynecological laparoscope to remove the ectopic pregnancy while preserving the fallopian tube. This approach is preferred when the patient desires to preserve fertility, as removing the affected tube can reduce the chances of conceiving in the future.
The laparoscopic procedure is typically performed under general anesthesia, and involves making several small incisions in the abdomen through which a laparoscope and surgical instruments are inserted. The laparoscope is equipped with a camera that allows the surgeon to visualize the affected area on a monitor, and the surgical instruments are used to remove the ectopic pregnancy.
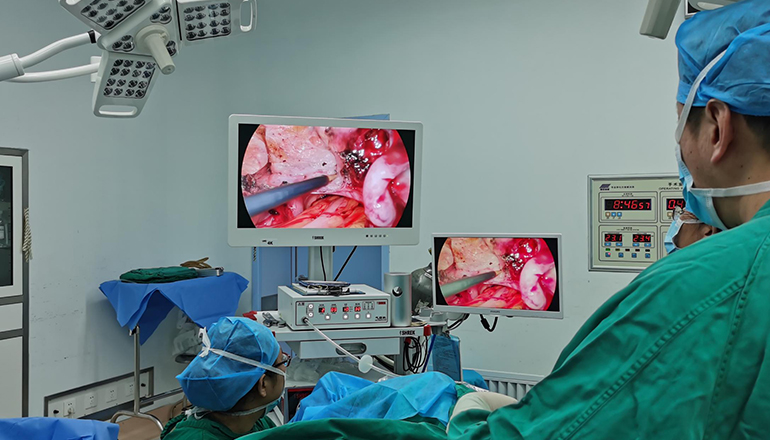
During the procedure, the surgeon will first examine the affected fallopian tube to determine the extent of the damage and to confirm the location of the ectopic pregnancy. If the tube is severely damaged or ruptured, it may need to be removed. However, if the tube appears to be healthy, the surgeon will attempt to remove only the ectopic pregnancy, leaving the tube intact.
After the ectopic pregnancy has been removed, the surgeon will inspect the remaining fallopian tube to ensure that there are no other abnormalities or blockages. If any issues are detected, additional surgical procedures may be required.
Following the laparoscopic procedure, the patient will be monitored for a period of time to ensure that there are no complications. Pain medication may be prescribed to manage any discomfort, and the patient may be advised to avoid strenuous activities for several days.
In conclusion, conservative operation of a tubal pregnancy using a gynecological laparoscope is a safe and effective approach for treating ectopic pregnancies while preserving fertility. The procedure involves removing the ectopic pregnancy while leaving the fallopian tube intact, and is typically performed under general anesthesia with a short recovery time.
Patients who undergo conservative operation for tubal pregnancy will need to follow up with their healthcare provider to monitor their recovery and ensure that there are no complications. They may need to have additional ultrasound or blood tests to confirm that the ectopic pregnancy has been completely removed and that the remaining tube is functioning properly.
In some cases, patients may experience recurrent ectopic pregnancies, especially if they have a history of tubal damage or other fertility issues. Women who have had a tubal pregnancy should consult with their healthcare provider before attempting to conceive again, as they may require additional testing or treatment to improve their chances of a successful pregnancy.
In summary, conservative operation of tubal pregnancy using a gynecological laparoscope is a safe and effective approach for treating ectopic pregnancies while preserving fertility. The laparoscopic procedure allows for a minimally invasive surgical approach, and can help reduce the risk of complications associated with traditional open surgery. However, each case of tubal pregnancy is unique, and patients should consult with their healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate treatment approach for their specific situation.
Leave a Comments