- Shanghai, China
- [email protected]
- +86-21-58189111
Pancreatoduodenectomy, also known as the Whipple procedure, is a surgical procedure used to treat tumors or other conditions of the pancreas, duodenum, or bile ducts. The procedure involves removing the head of the pancreas, the duodenum, a portion of the bile duct, and sometimes the gallbladder. Traditionally, pancreatoduodenectomy has been performed as an open surgery, but it can also be carried out using laparoscopic techniques, which offer several potential benefits, including reduced pain, shorter hospital stays, and faster recovery times.
Here are the general steps for carrying out pancreatoduodenectomy under laparoscope:
Preoperative preparation: The patient will receive general anesthesia and be positioned on the operating table. The surgical team will prepare the laparoscopic instruments and equipment, including a high-definition camera, laparoscopic graspers, scissors, and energy devices.
Creation of ports: The surgeon will make several small incisions in the abdomen and insert laparoscopic ports, which are small tubes that allow access for the laparoscopic instruments.
Exploration and mobilization: The surgeon will use the laparoscope to explore the abdominal cavity and identify the structures that need to be removed. The head of the pancreas, duodenum, and bile ducts will be mobilized and carefully dissected from surrounding tissues.
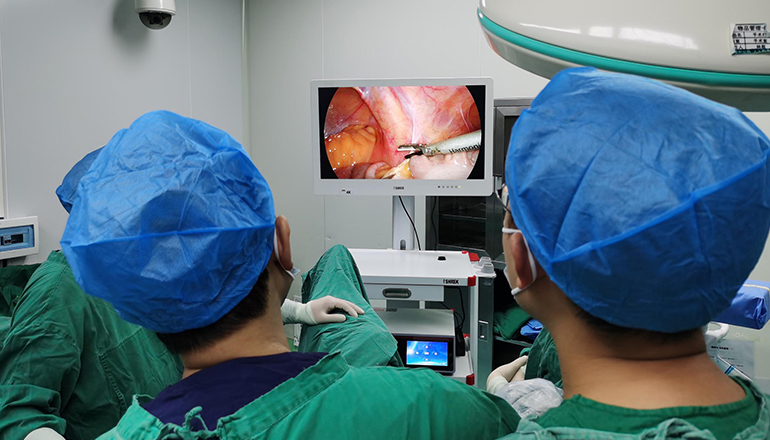
Division of vessels: The surgeon will identify and carefully divide the blood vessels that supply the organs being removed. This step requires a high level of skill and precision to avoid damage to nearby structures.
Removal of organs: Once the blood vessels have been divided, the surgeon will remove the head of the pancreas, duodenum, and bile ducts, as well as the gallbladder if necessary.
Reconstruction: The surgeon will then reconstruct the digestive system, using a variety of techniques depending on the extent of the resection. This may involve reattaching the remaining pancreas to the intestine, connecting the bile duct to the small intestine, and creating a new pathway for digestive fluids.
Closure: Once the reconstruction is complete, the surgeon will close the incisions using sutures or surgical staples.
Laparoscopic pancreatoduodenectomy requires a high level of technical skill and expertise. It is important for the surgical team to have extensive training and experience in laparoscopic techniques, as well as in the specific procedure being performed. The procedure may take longer to perform using laparoscopic techniques compared to open surgery, but it may offer advantages in terms of reduced pain, shorter hospital stays, and faster recovery times.
Laparoscopic pancreatoduodenectomy involves making small incisions in the abdomen, using a laparoscope to explore and mobilize the organs, dividing blood vessels, removing the organs, reconstructing the digestive system, and closing the incisions. It is a complex procedure that requires a highly skilled and experienced surgical team.
After the procedure is complete, the patient will be monitored in the recovery room for a period of time before being transferred to a hospital room. The patient will typically require a few days of hospitalization for observation and recovery. Pain medications and other medications may be prescribed to manage pain and prevent infection. The patient will also be given instructions on postoperative care, including wound care, dietary restrictions, and activity limitations.
Like any surgical procedure, laparoscopic pancreatoduodenectomy carries some risks, including bleeding, infection, and damage to surrounding organs. The risks and potential benefits of the procedure should be discussed with the patient before the procedure is performed.
In conclusion, laparoscopic pancreatoduodenectomy is a complex procedure that requires a highly skilled and experienced surgical team. It involves making small incisions in the abdomen, using a laparoscope to explore and mobilize the organs, dividing blood vessels, removing the organs, reconstructing the digestive system, and closing the incisions. While laparoscopic techniques may offer advantages compared to traditional open surgery, it is important to carefully consider the risks and benefits of the procedure and to select the appropriate approach based on the patient's individual needs and circumstances.
Leave a Comments