- Shanghai, China
- [email protected]
- +86-21-58189111
Suturing and knotting skills are critical for any surgeon performing laparoscopic surgery. Laparoscopic suturing is a technique used to close incisions or wounds inside the abdomen without requiring large incisions. The laparoscopic approach offers many benefits, including a faster recovery time, reduced pain and scarring, and lower risk of infection.
Suturing and knotting in laparoscopic surgery require the use of specialized instruments and techniques. In traditional open surgery, surgeons have direct access to the surgical field, allowing them to use their hands to manipulate and tie knots. In laparoscopic surgery, surgeons use long, thin instruments that are passed through small incisions to manipulate the surgical field. This makes it more challenging to suture and tie knots with precision.
There are several techniques used to suture and tie knots during laparoscopic surgery. One common technique is the "slip knot" or "instrument knot," which involves using an instrument to create a loop and then passing the suture through the loop to create a knot. Another technique is the "laparoscopic knot," which involves using an instrument to tie a knot on the suture without requiring a loop.
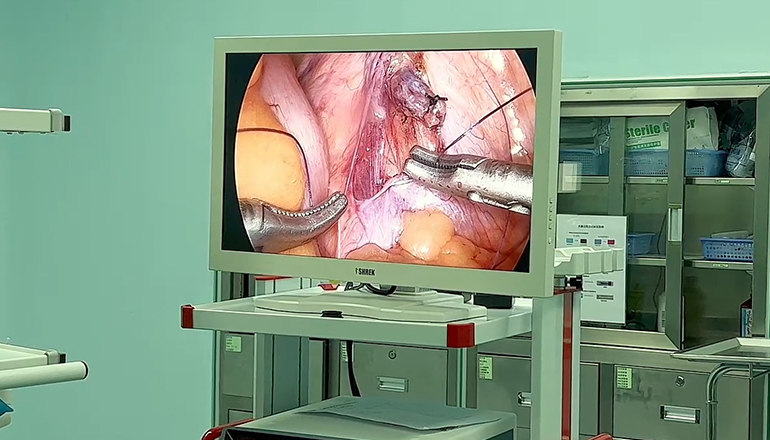
To perform laparoscopic suturing and knotting, surgeons need to have good hand-eye coordination and dexterity. They must be able to manipulate the instruments precisely to ensure that the sutures are placed accurately and knots are tied securely. It is important for surgeons to practice these skills extensively before performing laparoscopic surgery on patients.
Simulation training is a useful tool for surgeons to develop and improve their suturing and knotting skills under laparoscopy. Simulation training allows surgeons to practice these skills in a controlled environment without putting patients at risk. It provides an opportunity to learn from mistakes and develop proficiency before performing surgery on patients.
In conclusion, suturing and knotting skills are critical for surgeons performing laparoscopic surgery. Laparoscopic suturing and knotting require specialized instruments and techniques and demand good hand-eye coordination and dexterity. Simulation training can help surgeons develop and improve their skills before performing laparoscopic surgery on patients. With proper training and experience, surgeons can perform laparoscopic suturing and knotting with precision and accuracy, leading to better outcomes for their patients.
Additionally, technological advancements have improved the laparoscopic suturing and knotting process. New instruments and devices have been developed to make it easier to manipulate the surgical field and tie knots. For example, barbed sutures have been developed that eliminate the need for knot tying, which can save time and reduce the risk of knot failure.
In conclusion, suturing and knotting are essential skills for laparoscopic surgeons, and their proficiency can impact surgical outcomes. With the advancements in technology and training methods, laparoscopic suturing and knotting have become easier and more effective. It is important for surgeons to continue to develop their skills in these areas to provide the best possible care for their patients.
Leave a Comments