- Shanghai, China
- [email protected]
- +86-21-58189111
Hysteroscopic adhesiolysis or adhesectomy is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of intrauterine adhesions or scar tissue inside the uterus. This procedure is typically performed using a hysteroscope, which is a thin, lighted instrument that allows the surgeon to see inside the uterus and perform the necessary surgical procedures.
Intrauterine adhesions, also known as Asherman's syndrome, can occur due to a variety of factors, including uterine infections, uterine surgery, or repeated D&C (dilation and curettage) procedures. These adhesions can cause a range of symptoms, including infertility, abnormal menstrual bleeding, and recurrent miscarriage.
Hysteroscopic adhesiolysis is typically performed under general anesthesia, and the patient is usually discharged from the hospital on the same day. The procedure involves inserting the hysteroscope into the uterus through the cervix, and then using specialized instruments to remove the adhesions. The surgeon may also use a small balloon or other tools to help separate the adhesions from the uterine wall.
Following the procedure, the patient may experience some mild cramping and bleeding, which usually resolves within a few days. In some cases, antibiotics or pain medication may be prescribed to help manage any discomfort or infection.
The success of hysteroscopic adhesiolysis depends on several factors, including the severity and extent of the adhesions, the skill and experience of the surgeon, and the patient's overall health. In some cases, multiple procedures may be required to fully remove the adhesions and restore the normal functioning of the uterus.
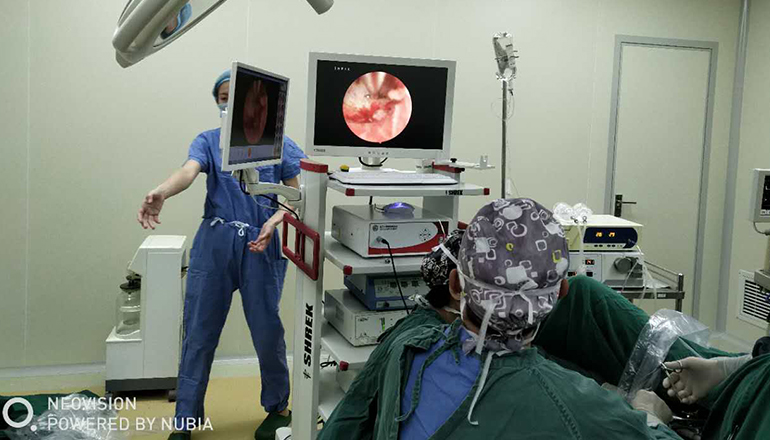
Hysteroscopic adhesiolysis is a safe and effective procedure for treating intrauterine adhesions and restoring fertility and normal menstrual function. It is important for patients to consult with a qualified gynecologist or reproductive specialist to determine if this procedure is appropriate for their individual needs and circumstances.
In addition, hysteroscopic adhesiolysis is often preferred over traditional open surgery as it is less invasive, has fewer complications, and allows for a quicker recovery time. However, there are certain situations where open surgery may be required if the adhesions are particularly severe or if the patient has other medical conditions that make hysteroscopy unsafe.
After hysteroscopic adhesiolysis, patients may be advised to wait a certain amount of time before attempting to conceive to allow the uterus to fully heal. The patient may also be advised to undergo fertility treatments, such as in vitro fertilization (IVF), to increase their chances of conception.
Overall, hysteroscopic adhesiolysis is a valuable tool in the treatment of intrauterine adhesions and can help improve the quality of life for women struggling with fertility issues or abnormal menstrual bleeding. With proper evaluation, diagnosis, and treatment planning, patients can undergo this procedure safely and effectively with the help of a skilled gynecologist or reproductive specialist.
Leave a Comments