- Shanghai, China
- [email protected]
- +86-21-58189111
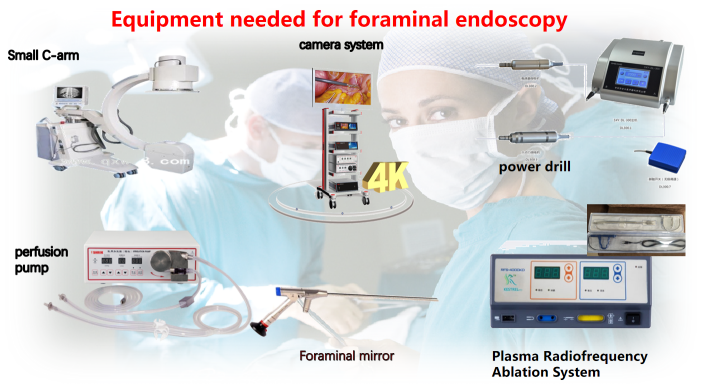
Similar to the spinal endoscope, the foramoscope is a tube equipped with light, which enters the intervertebral foramen from the side or the back of the patient's body (either flat or oblique), and performs surgery in the safe working triangle area. When surgery is performed outside the annulus fibrosus, the protruding nucleus pulposus, nerve roots, dural sac and hyperplastic bone tissue can be clearly seen under direct endoscopy. Then, various types of grasping forceps were used to remove the protruding tissue, microscopic bone removal, and radiofrequency electrodes to repair the damaged annulus fibrosus. The surgical trauma is small: the skin incision is only 7mm, the size of a soybean grain, the bleeding is less than 20ml, and only one stitch is sutured after the operation. It is the minimally invasive therapy for intervertebral disc herniation with the least trauma and the best effect in similar operations.
Principles of treatment
PTED removes the pressure on the nerve root by completely removing the prolapsed or prolapsed nucleus pulposus and hyperplastic bone outside the safety triangle of the intervertebral foramen and the annulus fibrosus of the intervertebral disc, and relieves the pain caused by the compression of the nerve. The surgical method is a spinal minimally invasive surgical system composed of a specially designed intervertebral foramen mirror and corresponding supporting spinal minimally invasive surgical instruments, imaging and image processing systems. At the same time of complete excision of protruding or prolapsed nucleus pulposus, bone hyperplasia can be removed, spinal stenosis can be treated, and the damaged annulus fibrosus can be repaired by radiofrequency technology.
Entry location
A: In cases of simple intervertebral disc herniation and partial prolapse, the posterolateral safe triangle approach is preferred.
B: The far lateral horizontal approach is suitable for the central giant protrusion.
C: Posterior or interlaminar approach is suitable for free or calcified patients
D: Applicable to almost all types of intervertebral disc herniation and some cases of bony stenosis
Leave a Comments