- Shanghai, China
- [email protected]
- +86-21-58189111
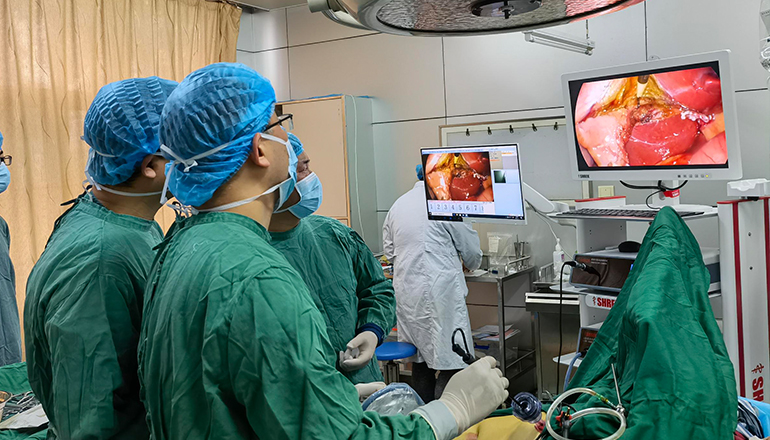
Endoscopy is a medical procedure that allows physicians to view the inside of a patient's body using an endoscope, a flexible tube with a camera and light source. Endoscopic cameras are essential for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes in various medical specialties, including gastroenterology, pulmonology, urology, gynecology, and otolaryngology.
There are different types of endoscopic cameras, each designed for specific medical applications. The following are some of the most common types of medical endoscopic cameras:
Fiberoptic cameras: These are the earliest type of endoscopic cameras, where the light is transmitted through optical fibers. Fiberoptic cameras are small and flexible, making them suitable for endoscopic procedures that require maneuvering through tight spaces.
Video cameras: These are the most commonly used endoscopic cameras in modern medicine. They use digital technology to produce high-quality images and videos of the inside of the patient's body. Video cameras come in different sizes and shapes, depending on the type of procedure and the patient's anatomy.
Capsule cameras: Capsule endoscopy is a non-invasive procedure that uses a tiny wireless camera in a capsule to take pictures of the digestive tract. The patient swallows the capsule, and the camera captures images as it moves through the patient's gastrointestinal tract.
C-arm cameras: These are used in interventional endoscopy procedures, where the physician needs to guide instruments to the target area. C-arm cameras provide real-time imaging to help the physician visualize the procedure and make precise movements.
3D cameras: These cameras provide three-dimensional images that can improve visualization and depth perception during endoscopic procedures. 3D cameras are particularly useful in complex procedures, such as laparoscopy and neurosurgery.
Multispectral cameras: These cameras use different wavelengths of light to provide additional information about the tissue being examined. Multispectral cameras can help physicians differentiate between healthy and abnormal tissue and detect early signs of disease.
Endoscopic cameras are essential tools in modern medicine, enabling physicians to visualize and treat the inside of the patient's body without invasive procedures. The type of endoscopic camera used depends on the medical specialty, the type of procedure, and the patient's anatomy.
Endoscopic cameras have revolutionized the way physicians diagnose and treat various medical conditions. They allow for earlier detection of diseases, less invasive surgeries, and faster recovery times for patients. Additionally, the development of new technologies, such as artificial intelligence and machine learning, is enabling endoscopic cameras to become even more sophisticated, providing physicians with more detailed information about the patient's condition.
However, despite the many benefits of endoscopic cameras, there are some potential risks and complications associated with their use, such as bleeding, infection, perforation, and anesthesia-related complications. Therefore, it is essential that patients undergo thorough evaluation and discussion of the risks and benefits before undergoing an endoscopic procedure.
In conclusion, endoscopic cameras have revolutionized modern medicine, allowing for earlier diagnosis and less invasive treatment of various medical conditions. There are several types of endoscopic cameras available, each designed for specific medical applications, including fiberoptic cameras, video cameras, capsule cameras, C-arm cameras, 3D cameras, and multispectral cameras. While endoscopic procedures have potential risks and complications, they offer significant benefits and are an essential tool for physicians in many medical specialties.
Leave a Comments