- Shanghai, China
- [email protected]
- +86-21-58189111
Laparoscopic splenectomy is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of the spleen through small incisions in the abdomen using a laparoscope. A laparoscope is a thin, flexible tube with a light and camera that allows the surgeon to view the internal organs on a monitor.
The spleen is an organ that plays a vital role in the immune system and helps to filter and remove old or damaged red blood cells from the body. However, in certain medical conditions such as idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP), hereditary spherocytosis, and lymphoma, the spleen may become enlarged and cause complications.
Laparoscopic splenectomy is a minimally invasive alternative to traditional open surgery, which involves a larger incision in the abdomen. The laparoscopic approach offers several advantages, including less postoperative pain, shorter hospital stay, faster recovery, and a better cosmetic outcome.
The procedure is typically performed under general anesthesia, and the patient is placed in a position that allows the surgeon to access the spleen through small incisions in the abdomen. The laparoscope and other specialized instruments are inserted through these incisions to visualize and remove the spleen.
The surgeon will first separate the spleen from surrounding tissues and blood vessels, taking care to avoid any damage to adjacent organs. Once the spleen is freed, it is placed in a bag and removed through one of the incisions.
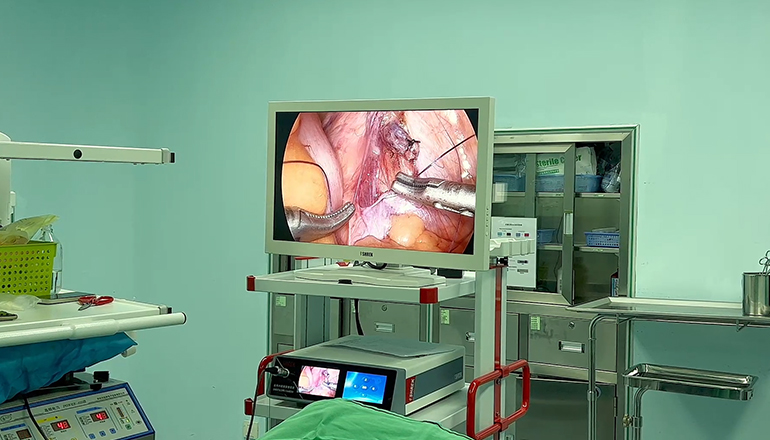
After the spleen is removed, the surgeon will inspect the remaining organs for any signs of bleeding or injury. The small incisions are then closed with sutures or surgical glue.
Patients typically recover faster from laparoscopic splenectomy than from traditional open surgery. They may experience some pain and discomfort in the first few days after surgery, which can be managed with medication. Patients are encouraged to walk and move around as soon as possible after surgery to help prevent blood clots and aid in recovery.
Some possible complications of laparoscopic splenectomy include bleeding, infection, injury to surrounding organs, and blood clots. However, these risks are generally low, and the benefits of the procedure often outweigh the risks.
In conclusion, laparoscopic splenectomy is a minimally invasive surgical technique that offers many advantages over traditional open surgery. It is a safe and effective treatment option for certain medical conditions that involve an enlarged or diseased spleen. Patients who undergo laparoscopic splenectomy can expect a shorter hospital stay, faster recovery, and a better cosmetic outcome than with traditional open surgery.
Furthermore, laparoscopic splenectomy has been shown to have a lower incidence of postoperative complications such as wound infections, incisional hernias, and bowel obstructions. Additionally, studies have demonstrated that laparoscopic splenectomy results in less blood loss and fewer blood transfusions compared to open surgery.
Overall, laparoscopic splenectomy is a safe and effective procedure that can provide patients with a less invasive treatment option for conditions involving an enlarged or diseased spleen. It offers numerous benefits, including less pain, shorter hospital stay, faster recovery, and a better cosmetic outcome. However, it is important to consult with a qualified surgeon to determine whether laparoscopic splenectomy is the most appropriate treatment option based on individual medical history and conditions.
Leave a Comments