- Shanghai, China
- [email protected]
- +86-21-58189111
Laparoscopic left adrenalectomy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to remove the left adrenal gland. The adrenal gland is a small, triangular-shaped gland located above each kidney. It plays an important role in regulating the body's stress response and the production of hormones such as adrenaline, cortisol, and aldosterone.
There are many reasons why a patient may require a left adrenalectomy. The most common reason is the presence of a tumor on the left adrenal gland. Tumors can be benign or malignant, and may cause symptoms such as high blood pressure, weight gain, and muscle weakness. Left adrenalectomy may also be used to treat conditions such as Cushing's syndrome, Conn's syndrome, and pheochromocytoma.
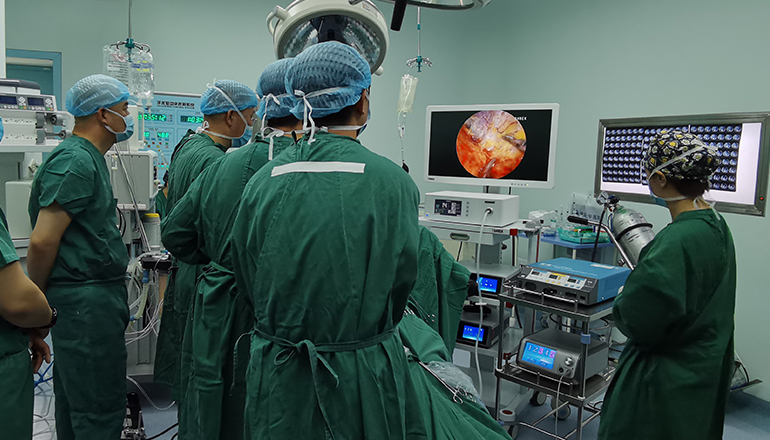
The laparoscopic left adrenalectomy procedure is typically performed under general anesthesia. During the procedure, the surgeon makes several small incisions in the abdomen and inserts specialized instruments and a camera called a laparoscope. The laparoscope allows the surgeon to see inside the abdomen and guide the instruments to the left adrenal gland. The gland is then carefully dissected and removed through one of the small incisions.
The laparoscopic approach offers many advantages over traditional open surgery. Because the incisions are small, patients typically experience less pain, scarring, and blood loss than with open surgery. They also tend to have shorter hospital stays and faster recovery times. Additionally, laparoscopic left adrenalectomy may be associated with lower rates of complications, such as wound infections, hernias, and blood clots.
After the procedure, patients will need to stay in the hospital for a short period of time for observation and monitoring. They may experience some discomfort and pain around the incision sites, but this can typically be managed with pain medication. Patients will also need to follow a special diet and activity restrictions for several weeks following the surgery to allow the incisions to heal properly.
Laparoscopic left adrenalectomy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to remove the left adrenal gland. It is typically used to treat tumors or other conditions that affect the left adrenal gland, and offers many advantages over traditional open surgery, including faster recovery times, lower rates of complications, and smaller incisions. If you or someone you know is considering a left adrenalectomy, speak with a healthcare professional to learn more about the potential risks and benefits and to determine whether the laparoscopic approach is appropriate for your individual needs.
In some cases, patients may require further treatment after a laparoscopic left adrenalectomy. For example, if the tumor removed from the left adrenal gland was malignant, patients may need to undergo chemotherapy or radiation therapy to eliminate any remaining cancer cells. Patients may also need to undergo regular follow-up appointments with their healthcare provider to monitor for any signs of recurrence or complications.
As with any surgical procedure, laparoscopic left adrenalectomy does carry some risks. These may include bleeding, infection, damage to surrounding organs or tissues, and complications associated with anesthesia. Patients should discuss the potential risks and benefits of the procedure with their healthcare provider prior to undergoing surgery.
Overall, laparoscopic left adrenalectomy is a safe and effective treatment option for patients with tumors or other conditions affecting the left adrenal gland. This minimally invasive procedure offers many benefits over traditional open surgery, including faster recovery times, lower rates of complications, and smaller incisions. If you or someone you know is considering a laparoscopic left adrenalectomy, speak with a healthcare professional to learn more about the potential risks and benefits and to determine whether it is an appropriate treatment option.
Leave a Comments