- Shanghai, China
- [email protected]
- +86-21-58189111
Splenectomy is a surgical procedure to remove the spleen. Laparoscopic splenectomy (LS) is a minimally invasive surgical technique that involves using a laparoscope to visualize and dissect the spleen. It is associated with less pain, shorter hospital stay, and faster recovery compared to open surgery. Here is a step-by-step guide on how to carry out LS:
Preoperative evaluation:
Before the operation, a thorough evaluation of the patient is necessary, including a detailed medical history, physical examination, blood tests, and imaging studies such as ultrasound and CT scans to assess the size and location of the spleen.
Surgical technique:
The procedure is performed under general anesthesia, and the patient is placed in a supine position with the legs apart. A laparoscope is introduced through a small incision in the umbilicus, and additional ports are placed in the abdomen to accommodate other surgical instruments. Carbon dioxide gas is then insufflated into the abdomen to create a working space.
The first step is to mobilize the spleen and expose its attachments to the surrounding structures. This involves dividing the ligamentum phrenicolienale and retracting the stomach and colon to expose the spleen. The splenic artery and vein are then identified and isolated using a combination of electrocautery and ultrasonic shears.
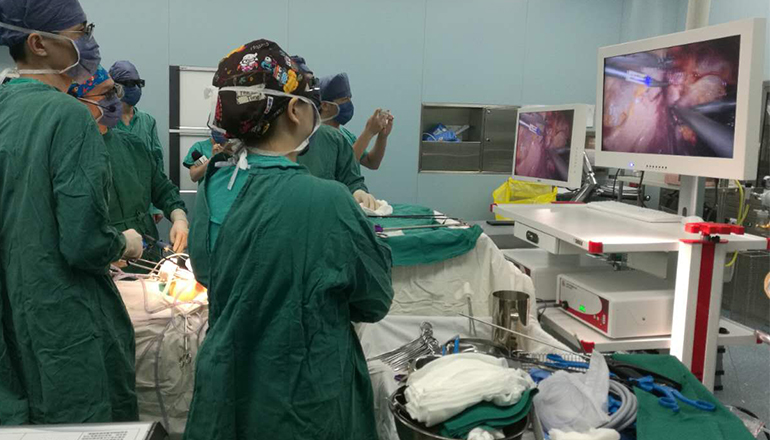
Next, the splenic artery and vein are divided and ligated using clips or a stapler to prevent bleeding. The spleen is then carefully dissected from its attachments to the diaphragm, pancreas, and left kidney using a combination of electrocautery and ultrasonic shears. The spleen is then placed into a specimen bag, and removed through one of the ports.
After the spleen is removed, the cut surface is inspected for hemostasis and any residual tissue is carefully dissected away. The remaining ports are then removed, and the abdominal incisions are closed.
Postoperative management:
Patients are typically kept in the hospital for several days following surgery to monitor their recovery. Pain medication, antibiotics, and anti-nausea medications are administered as needed. Patients are allowed to resume eating and drinking once bowel function has returned. A follow-up appointment with the surgeon is scheduled within several weeks after the surgery.
Complications:
As with any surgical procedure, there are potential complications associated with LS. These may include bleeding, infection, and injury to surrounding structures such as the pancreas, left kidney, and stomach. However, these risks are generally low and can be minimized with careful patient selection and surgical technique. In addition, most patients are able to return to their normal activities within a few weeks after surgery.
Long-term outcomes:
LS has been shown to have comparable long-term outcomes to open surgery in terms of overall survival and complication rates. However, long-term follow-up studies are still ongoing, and more data is needed to fully evaluate the efficacy of this approach.
LS is a minimally invasive surgical technique that can be used to safely and effectively remove the spleen. It offers several benefits over open surgery, including less pain, shorter hospital stay, and faster recovery. However, careful patient selection and meticulous surgical technique are essential to achieve optimal outcomes. Therefore, it is important to seek out an experienced surgical team who can provide the best possible care for patients undergoing LS.
It is worth noting that in some cases, LS may not be the best option. For example, if the spleen is very large or there is significant scarring or inflammation in the abdomen, open surgery may be necessary. Additionally, LS may not be recommended for patients with bleeding disorders or other medical conditions that increase the risk of complications.
Overall, LS is a safe and effective technique for splenectomy when performed by experienced surgeons. It can offer several advantages over traditional open surgery, including faster recovery times and reduced pain and scarring. If you are considering splenectomy, it is important to discuss your options with your healthcare provider to determine the best course of treatment for your individual needs.
Leave a Comments