- Shanghai, China
- [email protected]
- +86-21-58189111
Gynecological laparoscopic surgery is a minimally invasive surgical technique that utilizes a laparoscope, a thin, lighted tube with a camera, to view and operate on the internal organs of the pelvic cavity through small incisions. Gynecological laparoscopy is commonly used to diagnose and treat a variety of gynecological conditions such as endometriosis, fibroids, ovarian cysts, and infertility. Here are some basic operation skills for gynecological laparoscopic surgery:
Proper patient positioning: The patient is positioned on the operating table in a supine position with the legs elevated and flexed at the knees to allow access to the pelvic area. The patient's arms are tucked at her sides to prevent injury during the procedure.
Establishment of pneumoperitoneum: A small incision is made near the navel, and a needle is inserted into the abdominal cavity to introduce carbon dioxide gas, creating a pneumoperitoneum. This allows the surgeon to visualize the pelvic organs more clearly and provides working space for the laparoscope and surgical instruments.
Placement of trocars: Trocars are specialized ports that allow for the insertion of surgical instruments into the abdominal cavity. Usually, two or three trocars are placed through small incisions in the lower abdomen, which provide access for the laparoscope and other instruments.
Visualization: The laparoscope is inserted through one of the trocars and provides a magnified, high-definition view of the pelvic organs on a monitor. The surgeon uses this view to identify any abnormalities, such as cysts or adhesions.
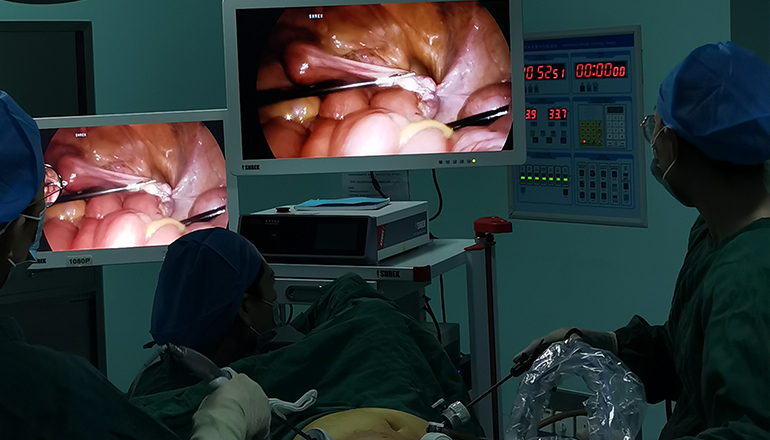
Dissection and tissue removal: Once the surgeon has identified any abnormal tissue or structures, they may use specialized instruments to dissect and remove them. These instruments include scissors, graspers, and cautery devices.
Hemostasis: Hemostasis is the process of stopping bleeding. The surgeon may use bipolar cautery, clips, or other hemostatic devices to control bleeding during the procedure.
Closure: Once the procedure is complete, the instruments and laparoscope are removed, and the trocar sites are closed with sutures or staples.
Postoperative care: Patients are typically discharged the same day or the day after the procedure. They may experience some discomfort and bloating for a few days after the surgery, but these symptoms typically resolve quickly. Patients are advised to avoid strenuous activity for a week or two after the surgery and to follow any other instructions provided by their surgeon.
In summary, gynecological laparoscopic surgery is a minimally invasive surgical technique that requires specialized training and skill. The surgeon must have a deep understanding of the anatomy of the pelvic area and be able to use specialized instruments to perform the procedure safely and effectively.
Furthermore, to become proficient in gynecological laparoscopic surgery, surgeons require extensive training, which includes both theoretical and practical components. They should complete a residency program in obstetrics and gynecology and then undertake specialized training in laparoscopic surgery through fellowships or other training programs.
Additionally, the surgeon must have an in-depth understanding of the indications, contraindications, and potential complications associated with laparoscopic surgery. They must also be able to recognize and manage complications that may arise during or after the surgery.
In conclusion, gynecological laparoscopic surgery is a valuable tool for the diagnosis and treatment of a variety of gynecological conditions. It offers numerous advantages over traditional open surgery, including less pain, faster recovery, and better cosmetic results. To perform this surgery, surgeons must have a deep understanding of the pelvic anatomy, specialized training, and advanced surgical skills. With proper training and experience, gynecological laparoscopic surgery can provide excellent outcomes for patients.
Leave a Comments